Page Not Found
Page not found. Your pixels are in another canvas.
A list of all the posts and pages found on the site. For you robots out there is an XML version available for digesting as well.
Page not found. Your pixels are in another canvas.
About me
This is a page not in th emain menu
Published:
InstaDeep: Exact Combinatorial Optimisation with Deep Reinforcement Learning (Blog post about the reinforcement learning for discrete optimisation project I worked on during an internship at InstaDeep, which ultimately resulted in a AAAI paper and oral.)
Published:
Elsevier: Advancing Data Center Networking through Open Access (Interview with me about the development of our TrafPy tool for generating custom and reproducible network traffic.)
Published:
ITPro: Why the Future Needs Optical Data Centres (Article featuring our research on optical switching.)
Published:
The Engineer: Overload Information (Cover story featuring our research on optical switching.)
Published:
This was a conversation piece co-authored by myself and my colleague Zacharaya Shabka in an attempt to outline the motivation behind making data centres all-optical for a broad audience.
Published:
These are the notes I am gradually building out for various parts of the background theory I need for my Ph.D. project in data centre networks. They are incomplete and periodically updated.
Published:
Modern augmented and virtual reality systems such as Oculus VR, Magic Leap and HoloLens products are fundamentally unfit for purpose because they use 2D projection which leads to eye fatigue and a lack of immersive experience for the user. Holography is the only way to produce truly 3D images, and could therefore emerge as the leading technology for such display systems. Historically to have large field-of-view holographic displays, engineers had to use either smaller spatial light modulators or telescope de-magnification techniques. This resulted in uncomfortably small and often impractical display sizes. In collaboration with the University of Cambridge and holographic display company VividQ, this project saw the development of a system capable of expanding the eyebox without compromising on display size, signficantly improving the usability and quality of 3D holographic displays.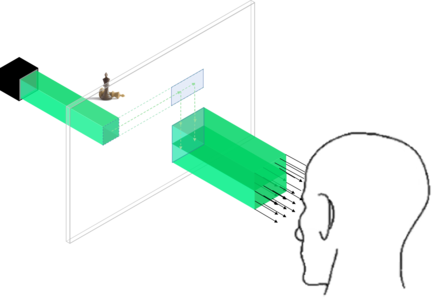
Published:
Autonomous driving holds the promise of reducing traffic accidents by designing safe, robust, accurate and intelligent agents. In this introductory-level competition, Huawei open-accessed their traffic perception simulation system with which competitors had 6 weeks to design, train and test a single-agent navigating roads and traffic. My team attempted to use the NeuroEvolution of Augmenting Topologies (NEAT) genetic algorithm for the agent policy trained with a reinforcement learning framework, however performance was ultimately not good due to poor generalisation to unseen scenarios.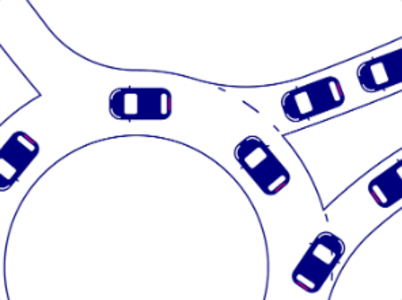
Published:
Software to detect network intrusions protects a computer network from unauthorised users, including perhaps insiders. The KDD dataset from the 1999 DARPA Intrusion Detection Evaluation Program competition contains roughly 5 million network connection request fingerprints split into 4 broad categories (DoS, R2L, U2R and probing attacks) which can be further sub-divided into 23 forms of attack. Using a standard sequential neural network with 3 hidden layers, a model was trained with a supervised learning framework in a client-server architecture to detect malicious network requests with 99.99% accuracy.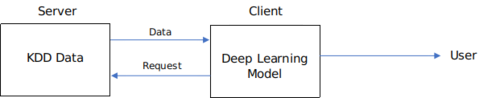
Published:
Using embedded systems hardware can be more complex to programme, but can bring benefits in terms of costs and power consumption. This project saw the development of a prototype ‘smart ski boot’ that could be used for more accurate, in-depth and cheap ski technique instruction than is deliverable by expensive human instructors, who typically charge £500-700 a day. This stands to benefit not only skiers who will save money in tuition fees and receive superior teaching, but also the ski industry, from restauranteurs to equipment providers, whose customer base will increase as fewer people are priced out of the sport.
Published:
(Paper One) (GitHub) Low-latency, high-bandwidth, ultra-scalable optical circuit switched networks can address the limitations of current compute clusters and enable the deployment of next-generation high-performance clusters and data centres. In particular, machine learning workloads present a unique opportunity for which to develop specialised circuit-based clusters because they are predictable, periodic, and consist mostly of large network flows. Furthermore, trillion-parameter learning models are being developed with final test performances capped primarily by the model size; a characteristic which, in the ‘strong scaling’ case, is limited by the bandwidth of the network connecting the cluster’s servers. In this work, we aim to address the challenge of how to make resource management decisions (from computation graph partitioning and placement to server allocation and scheduling) when training massive models on an optical cluster with distributed deep learning. By framing the problem as a Markov decision process where sequential actions must be taken to maximise some reward (such as minimising the overall job completion time), a graph neural network can be trained from scratch with end-to-end reinforcement learning to allocate the cluster’s resources near-optimally. We are in the process of developing a suite of cluster environments, graph neural network models, and reinforcement learning algorithms in order to achieve this, and we hope to demonstrate both good performance and the ability to scale to large networks and jobs. 
Published:
(Paper One) (Paper Two) (Paper Three) (GitHub) (Documentation) One of the primary bottlenecks to all-optical data centre networks is the lack of a packet-timescale switch. This project saw the application of AI techniques to switch semiconductor optical amplifiers in just half a nanosecond. AI beat the previous world-record by an order of magnitude and, for the first time, offered the potential to be scaled to thousands of switches in a real data centre.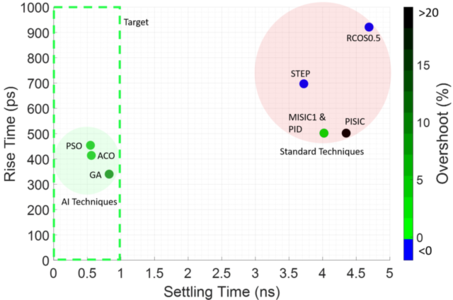
Published:
(Paper One) (Paper Two) (GitHub) Optimisation problems are search problems where a solution which maximises some objective is being sought amongst a search space. Combinatorial optimisation (CO) is an optimisation sub-category where the solution being sought is a discrete variable (e.g. an integer, a graph, a set, etc.) amongst a finite (or countably infinite) space of possible solutions. Many real-world problems fall under the broad category of CO, from network routing and scheduling to protein folding and fundamental science. However, with many CO problems being NP-hard, solving non-trivial instance sizes in reasonable time frames is a significant challenge. Although CO solvers were studied and designed extensively in the latter half of the 20th, recent years have seen a resurgance in their academic study with the application of machine learning to solving CO problems. This work saw the application of graph neural networks and reinforcement learning to learn to solve graph-based combinatorial optimisation problems from scratch. This was done through the design of two new machine learning algorithms. The first achieved state-of-the-art scalability for learned heuristic solutions, and the second enabled the integration of reinforcement learning into exact branch-and-bound solvers. These are important steps towards establishing machine learning as the go-to approach for solving CO problems, which will unlock advances in a plethora of real-world applications. 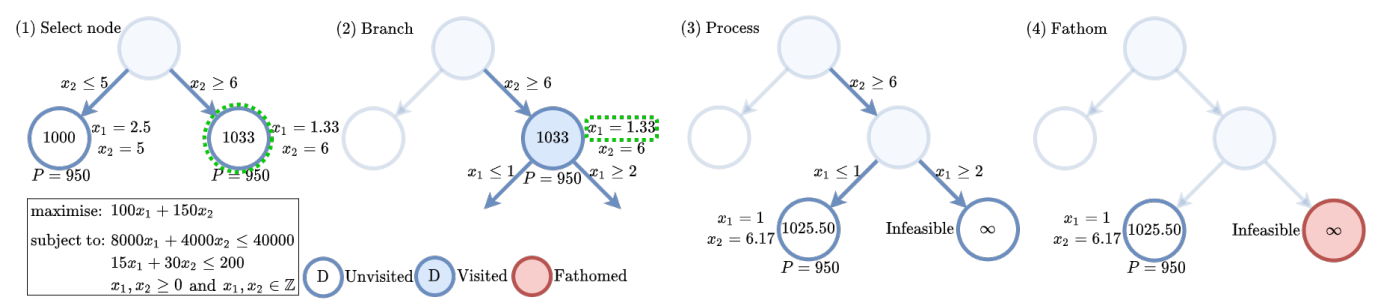
Published:
(Paper One) (Paper Two) (Paper Three) (GitHub) (Documentation) Data related to communication networks is often sensitve and proprietary. Consequently, many networking academic papers are published without open-accessing the network traffic data that was used to obtain the results, and when they are published the datasets are often too limited for data-hungry applications such as reinforcement learning. In an effort to aid reproducibility, some authors release characteristic distributions which broadly describe the underlying data. However, these distributions are often not analytically described and may not fall under the classic ‘named’ distributions (Gaussian, log-normal, Pareto etc.). As a result, other researchers find themselves using unrealistically simple uniform traffic distributions or their own distributions which are difficult to universally benchmark. This project saw the development of an open-access network traffic generation tool for (1) standardising the traffic patterns used to benchmark networking systems, and (2) enabling rapid and easy replication of literature distributions even in the absence of raw open-access data.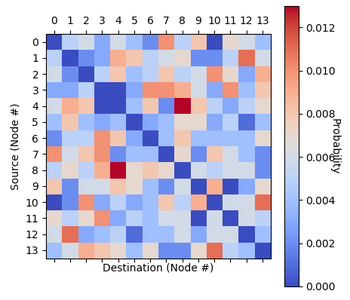
Published in Journal of Lightwave Technology (JLT), 2020
Recommended citation: C. W. F. Parsonson, Z. Shabka, W. K. Chlupka, B. Goh and G. Zervas, "Optimal Control of SOAs with Artificial Intelligence for Sub-Nanosecond Optical Switching", Journal of Lightwave Technology (JLT), 2020 https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9124678
Published in Photonic Networks and Devices, 2021
Recommended citation: Joshua L. Benjamin, Christopher W. F. Parsonson, and G. Zervas "Benchmarking Packet-Granular OCS Network Scheduling for Data Center Traffic Traces", Photonic Networks and Devices, 2021 https://opg.optica.org/abstract.cfm?uri=Networks-2021-NeW3B.3
Published in Optics Express, 2021
Recommended citation: T. Gerard, C. W. F. Parsonson, Z. Shabka, B. Thomsen, P. Bayvel, D. Lavery and G. Zervas, "AI-Optimised Tuneable Sources for Bandwidth-Scalable, Sub-Nanosecond Wavelength Swithching", Optics Express, 2021 https://opg.optica.org/oe/fulltext.cfm?uri=oe-29-7-11221&id=449558
Published in European Conference and Exhibition on Optical Communication (ECOC), 2022
Recommended citation: H. Alkharsan, C. W. F. Parsonson, Z. Shabka, X. Mu, A. Ottino and G. Zervas, "Optimal and Low Complexity Control of SOA-Based Optical Switching with Particle Swarm Optimisation", ECOC-22: European Conference and Exhibition on Optical Communication, 2022 https://opg.optica.org/abstract.cfm?uri=ECEOC-2022-Tu3C.5
Published in Optical Fiber Communications Conference and Exhibition (OFC), 2022
Recommended citation: J. L. Benjamin, A. Ottino, C. W. F. Parsonson and G. Zervas, "Traffic Tolerance of Nanosecond Scheduling on Optical Circuit Switched Data Centre Networks", OFC-22: Optical Fiber Communications Conference and Exhibition, 2022 https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9748332
Published in Optical Switching and Networking, 2022
Recommended citation: C. W. F. Parsonson, J. L. Benjamin and G. Zervas, "Traffic Generation for Benchmarking Data Centre Networks", Optical Switching and Networking, 2022 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1573427722000315
Published in Under peer review, 2022
Recommended citation: C. W. F. Parsonson and G. Zervas "Partitioning Distributed Compute Jobs with Reinforcement Learning and Graph Neural Networks", Under peer review, 2022 Link to be added soon.
Published in Under peer review, 2022
Recommended citation: T. D. Barrett, C. W. F. Parsonson and A. Laterre "Learning to Solve Combinatorial Graph Partitioning Problems via Efficient Exploration", Under peer review, 2022 https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.14105
Published in Proceedings of the Thirty-Seventh AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), 2023
Recommended citation: C. W. F. Parsonson, A. Laterre and T. D. Barrett "Reinforcement Learning for Branch-and-Bound Optimisation using Retrospective Trajectories", AAAI-23: Proceedings of the Thirty-Seventh AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2023 https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.14345?context=cs
Published in Under peer review, 2023
Recommended citation: J. L. Benjamin, C. W. F. Parsonson, and G. Zervas "A Data Scheduling Unit for Nanosecond Optical Data Center Networks", Under peer review, 2023 Link to be added soon
Published in Journal of Lightwave Technology (JLT), 2023
Recommended citation: Y. Liu, J. L. Benjamin, C. W. F. Parsonson, and G. Zervas "A Hybrid Beam Steering Free-Space and Fiber Based Optical Data Center Network", Journal of Lightwave Technology (JLT), 2023 Link to be added soon
Published in Optical Fiber Communications Conference and Exhibition (OFC), 2023
Recommended citation: C. W. F. Parsonson, Joshua L. Benjamin, and G. Zervas "A Vectorised Packing Algorithm for Efficient Generation of Custom Traffic Matrices", OFC-23: Optical Fiber Communications Conference and Exhibition, 2023 https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.09970
Published:
This is a description of your talk, which is a markdown files that can be all markdown-ified like any other post. Yay markdown!
Published:
This is a description of your conference proceedings talk, note the different field in type. You can put anything in this field.
Undergraduate course, University 1, Department, 2014
This is a description of a teaching experience. You can use markdown like any other post.
Workshop, University 1, Department, 2015
This is a description of a teaching experience. You can use markdown like any other post.